Learning Outcomes
i. Define projectile motion and its characteristics.
ii. Understand the concept of the horizontal component of velocity (VH) in projectile motion.
iii. Explain why the horizontal component of velocity remains constant throughout the flight of a projectile.
iv. Recognize that gravity affects only the vertical component of velocity, leaving the horizontal component unaffected.
v. Apply the concept of constant horizontal velocity to solve projectile motion problems.
Introduction
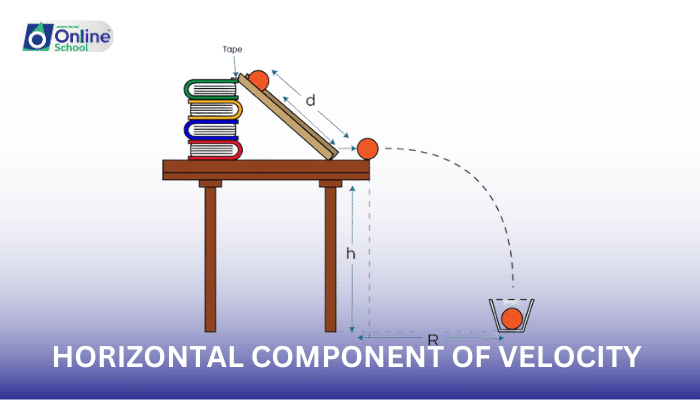
As we observe objects soaring through the air, from thrown balls to launched rockets, we witness projectile motion in action. This fascinating phenomenon involves an object being launched into the air, typically at an angle, and embarking on a journey influenced by gravity. While gravity plays a crucial role in shaping the projectile's path, one aspect of its motion remains unwavering – the horizontal component of velocity.
i. The Horizontal Component of Velocity: A Constant Companion
The horizontal component of velocity (VH) represents the projectile's speed in the horizontal direction. Remarkably, this component remains unchanged throughout the projectile's flight, assuming no air resistance. This constancy stems from the fact that gravity, the primary force acting on the projectile, only affects its motion in the vertical direction.
ii. Gravity's Grip on Vertical Motion
Gravity, the force that keeps us grounded, exerts its influence on the projectile's vertical motion, causing its vertical velocity to change continuously. As the projectile ascends, its vertical velocity decreases, eventually reaching zero at the maximum height. During descent, the vertical velocity increases, pulling the projectile back towards the ground.
iii. Horizontal Motion: Immune to Gravity's Pull
In contrast to the vertical motion, the horizontal motion of the projectile remains unaffected by gravity. This immunity arises from the absence of any horizontal force acting on the projectile. Since gravity only pulls downwards, it has no influence on the projectile's horizontal speed.
iv. The Significance of Constant Horizontal Velocity
The constant horizontal velocity provides a valuable tool for analyzing projectile motion. By recognizing that the horizontal component remains unchanged, we can simplify calculations and gain insights into the projectile's trajectory.
v. Applying Constant Horizontal Velocity in Problem-Solving
When solving projectile motion problems, we can utilize the concept of constant horizontal velocity to determine various aspects of the projectile's motion. For instance, we can calculate the horizontal displacement, the time of flight, or even the projectile's velocity at any point in its flight path.
The unwavering horizontal component of velocity in projectile motion is a testament to the interplay between forces and motion. While gravity shapes the projectile's vertical journey, the absence of horizontal forces allows the horizontal motion to proceed undisturbed. Understanding this concept not only deepens our grasp of projectile motion but also serves as a reminder of the intricate balance of forces that govern our physical world.